Oesophago-gastric Cancer Surgery
Oesophagectomy
Oesophagectomy is an operation performed usually for the treatment of oesophageal cancer. Very rarely is it performed for patients with benign disease. Oesophageal cancer is an increasing problem in Australia and oesophagectomy offers the only chance of cure.
Indications
Oesophageal cancer is the most common indication for surgery. Often chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy are recommended pre-operatively and occasionally post-operatively. All patients will be discussed at a Multi-Disciplinary Team Meeting.
Other indications include benign diseases such as peptic strictures, benign lesions (GIST) or achalasia.
Surgery:
There are generally 2 types of surgery offered depending on the location of the tumour:
- 2 Stage Oesophagectomy (Ivor-Lewis) – involves abdominal and thoracic (chest) incisions. These are generally performed laparoscopically (keyhole) for the abdomen and through an open (larger) incision in the chest.
- 3 Stage Oesophagectomy (McKeown) – involves abdominal, thoracic and neck incisions. Various parts of this operation are performed thorascopically, laparoscopically and open depending on your surgeon.
Total Upper GI Surgery will recommend one operative approach based on your clinical symptoms, previous surgery and medical problems. It is your decision to proceed with surgery. Surgery will typically involve a 10-14 days stay in hospital.
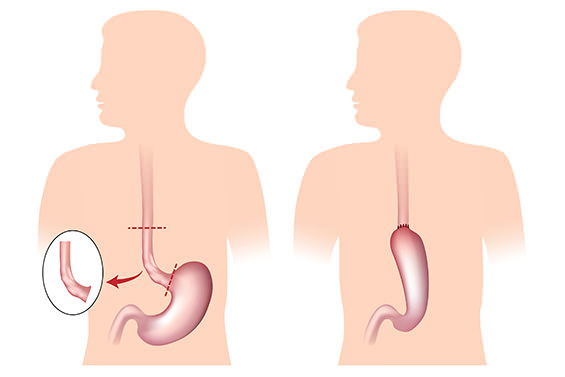
Risks:
Oesophagectomy is a large operation which may result in minor or major complications (anastomotic or chyle leak). Longer term consequences of oesophagectomy include reflux, weight loss, fatigue, lower appetite and difficulty swallowing.
Gastrectomy
Gastrectomy is an operation usually performed for the treatment of gastric cancer. It is however, occasionally performed for benign conditions such a ulcers, bleeding or benign tumours. Gastric cancer is an uncommon cancer in the Australian population.
Indications
Gastric cancer is the most common indication for surgery. Often chemotherapy will be recommended both pre- and post-operatively. A staging laparoscopy (keyhole) will be performed prior to commencing treatment. All cancer patients will be discussed at a Multi-Disciplinary Team Meeting.
Surgery
Surgery will typically be performed laparoscopically, however some will require open surgery (larger incision in upper abdomen). Most patients will be admitted for 5-10 days following surgery. Surgery involves removing part or all of the stomach and joining bowel to the remaining stomach or oesophagus (food pipe).

Risks:
May include: Pain, Bleeding, Anastomotic leak, Dumping, Weight loss, Lung/heart complications, Clots


